- [ECAI'25] When Secure Aggregation Falls Short: Achieving Long-Term Privacy in Asynchronous Federated Learning for LEO Satellite Networks [DOI: 10.3233/FAIA250920]
M. Elmahallawy and T. Luo
28th European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Oct 2025, vol. 413, pp. 1099-1106.
- [PAKDD'25w] Unlocking Neural Transparency: Jacobian Maps for Explainable AI in Alzheimer's Detection [arXiv] [slides]
Y. Mustafa, M. Elmahallawy, and T. Luo
2025 PAKDD workshop on Pattern mining and Machine learning for Bioinformatics, June 2025. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 15835, pp. 229–242.
Best Paper Award [University News]
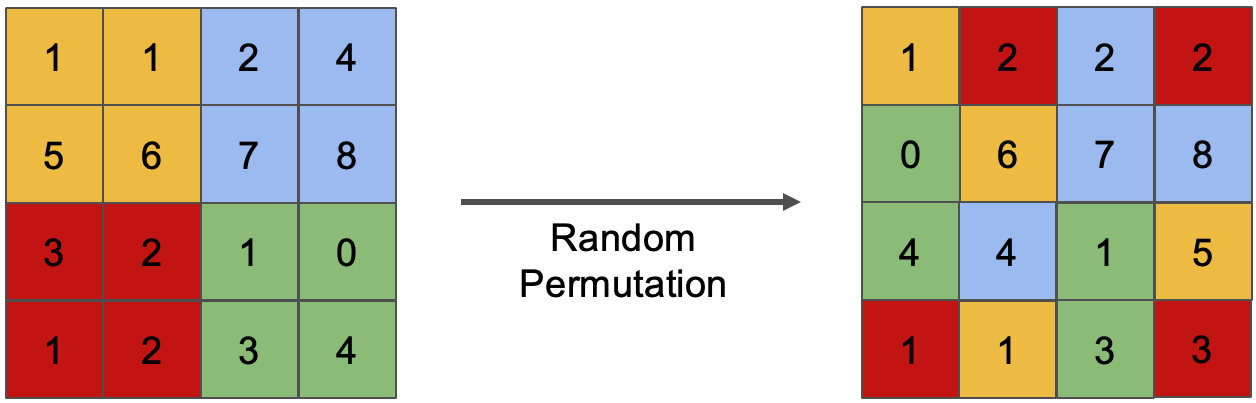
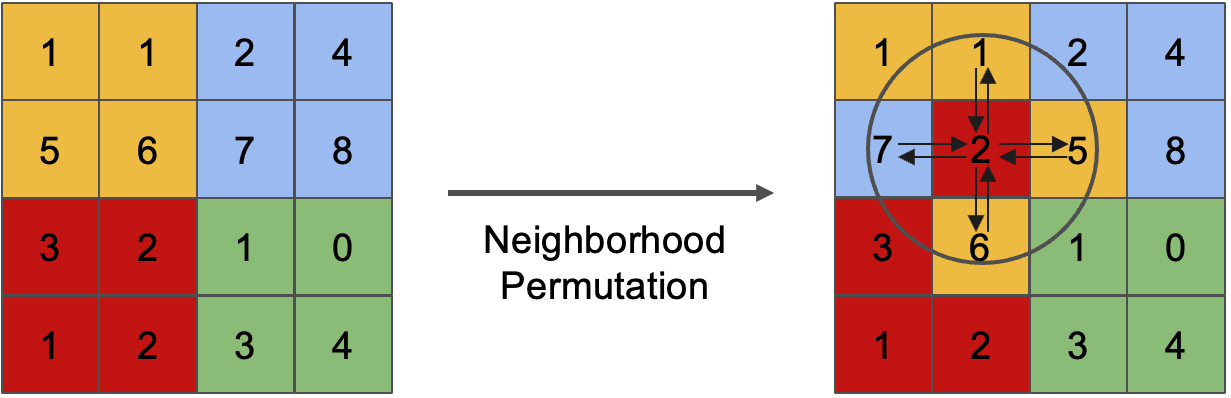
- [PAKDD'25] Enabling Heterogeneous Adversarial Transferability via Feature Permutation Attacks [arXiv] [slides]
T. Wu and T. Luo
29th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD), June 2025. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 15873, pp. 39–51.
Acceptance rate: overall 24% (168/696); main track 24% (134/557).
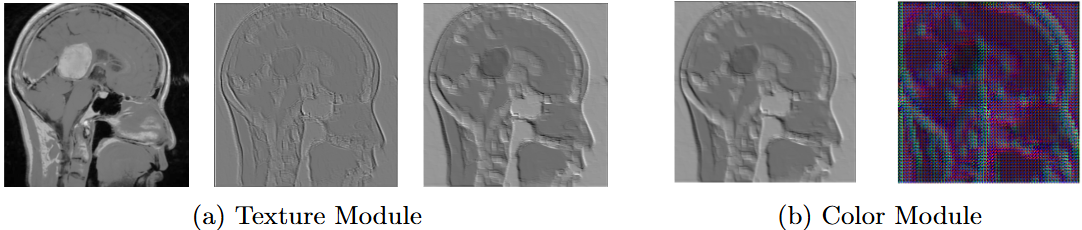
- [BigData'24] Efficient Brain Imaging Analysis for Alzheimer's and Dementia Detection Using Convolution-Derivative Operations [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/BigData62323.2024.10825276]
Y. Mustafa, M. Elmahallawy, and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), December 2024, pp. 6420-6429.
- [PAKDD'24] Adversarial-Robust Transfer Learning for Medical Imaging via Domain Assimilation [arXiv] [slides] [DOI: 10.1007/978-981-97-2238-9_26]
X. Chen and T. Luo
28th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD), May 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 14648, pp. 335–349.
Acceptance rate: 18.5% (133/720) (oral presentations)
Best Paper Runner-Up Award (0.28%; 2/720) [University News]
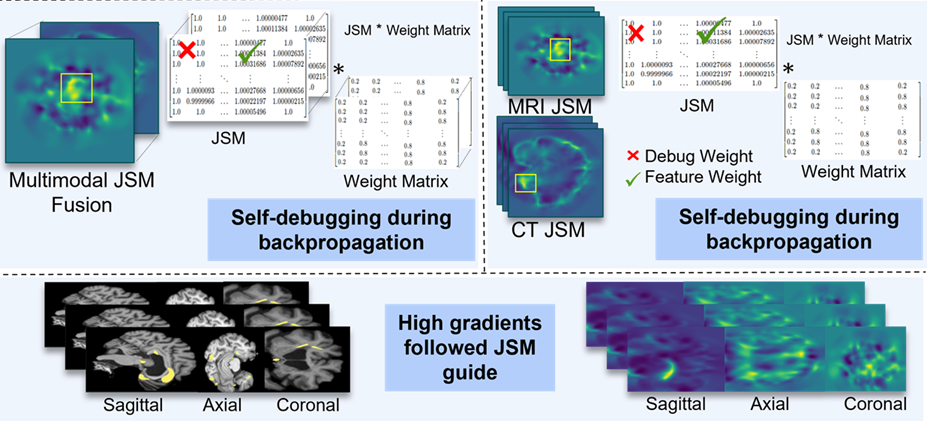
- [PAKDD'24] Unmasking Dementia Detection through Masking Input Gradients: A JSM Approach to Model Interpretability and Precision [arXiv] [poster version] [DOI: 10.1007/978-981-97-2259-4_6]
Y. Mustafa and T. Luo
28th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD), May 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 14647, pp. 75–90.
Acceptance rate: 24.3% (175/720; 133 oral + 42 poster presentations, both published the same in proceedings as full papers)
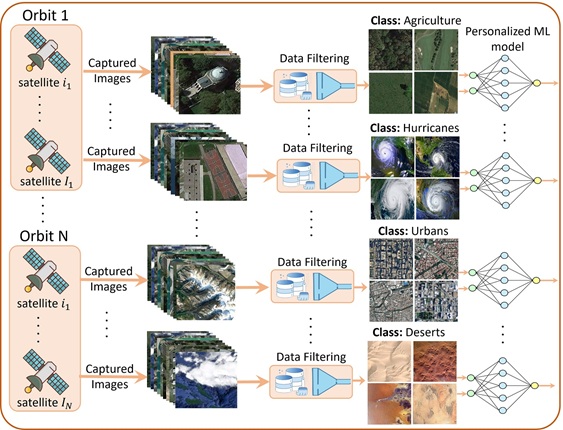
- [PerCom'24] Stitching Satellites to the Edge: Pervasive and Efficient Federated LEO Satellite Learning [arXiv] [slides] [DOI: 10.1109/PerCom59722.2024.10494442]
M. Elmahallawy and T. Luo
22nd IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), March 2024, pp. 80-89.
Acceptance rate: 14.5% (23/158)
Among the 158 full submissions, 15 (including ours) were accepted as full papers and 8 accepted as short papers.
Best Paper Runner-Up Award (1.3%; 2/158)
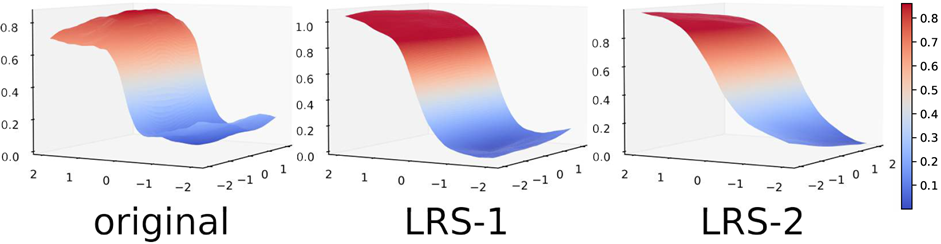
- [AAAI'24] LRS: Enhancing Adversarial Transferability through Lipschitz Regularized Surrogate [arXiv] [poster version] [code] [DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v38i6.28430]
T. Wu, T. Luo, and D. C. Wunsch
38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 6135-6143, February 2024.
Acceptance rate: 19% (2342/12100)
Among the 12100 submissions to the main track, 2238 were desk-rejected.
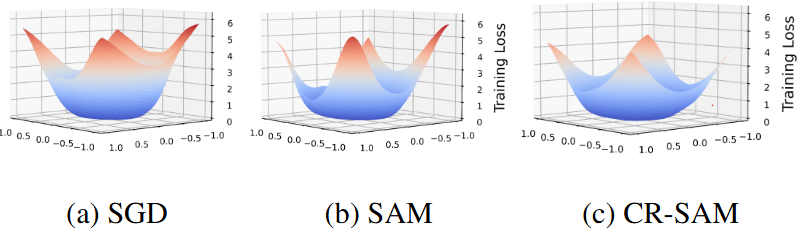
- [AAAI'24] CR-SAM: Curvature Regularized Sharpness-Aware Minimization [arXiv] [poster version] [code] [DOI: 10.1609/aaai.v38i6.28431]
T. Wu, T. Luo, and D. C. Wunsch
38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 6144-6152, February 2024.
Acceptance rate: 19% (2342/12100)
Among the 12100 submissions to the main track, 2238 were desk-rejected.
- [Healthcom'23] Diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease using Early-Late Multimodal Data Fusion with Jacobian Maps [arXiv] [slides] [DOI: 10.1109/Healthcom56612.2023.10472348]
Y. Mustafa and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on E-health Networking, Application & Services (Healthcom), December 2023, pp. 49-55.
- [Globecom'23]
Secure and Efficient Federated Learning in LEO Constellations using Decentralized Key Generation and On-Orbit Model Aggregation [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/GLOBECOM54140.2023.10436841]
M. Elmahallawy, T. Luo, and M. I. Ibrahem
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), December 2023, pp. 5727-5732.
- [TrustCom'23] Crowdsourcing-based Model Testing in Federated Learning [pdf] [DOI: 10.1109/TrustCom60117.2023.00048]
Y. Yi, H. Lv, T. Luo, L. Liu, L. Cui
IEEE 22nd International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), November 2023, pp. 207-213.
- [ICIP'23] GNP Attack: Transferable Adversarial Examples via Gradient Norm Penalty [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/ICIP49359.2023.10223158]
T. Wu, T. Luo, and D. C. Wunsch
30th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), October 2023, pp. 3110-3114.
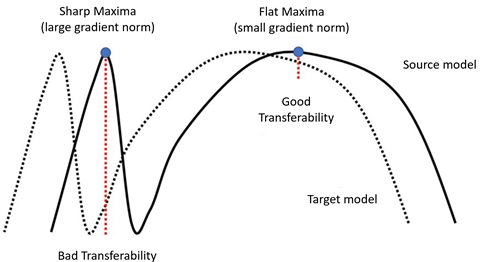
- [MetroXAINE'23] A Brain-Computer Interface Augmented Reality Framework With Auto-Adaptive SSVEP Recognition
Y. Mustafa, M. Elmahallawy, T. Luo, S. Eldawlatly
IEEE International Conference on Metrology for eXtended Reality, Artificial Intelligence and Neural Engineering, October 2023.
- [EDGE'23] LightESD: Fully-Automated and Lightweight Anomaly Detection Framework for Edge Computing [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/EDGE60047.2023.00032]
R. Das and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on Edge Computing (EDGE), July 2023, pp. 150-158.
Acceptance rate: 17% (full paper)
- [MDM'23] One-Shot Federated Learning for LEO Constellations that Reduces Convergence Time from Days to 90 Minutes [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/MDM58254.2023.00020]
M. Elmahallawy and T. Luo
24th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM), July 2023, pp. 45-54.
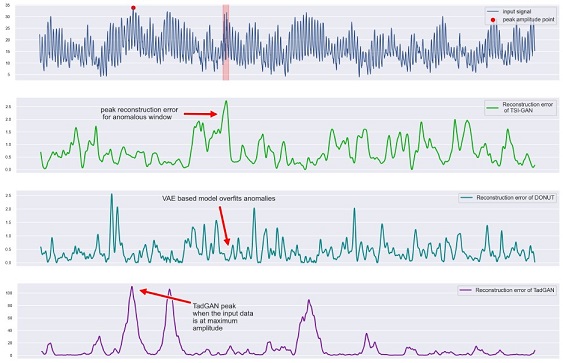
- [PAKDD'23] TSI-GAN: Unsupervised Time Series Anomaly Detection using Convolutional Cycle-Consistent Generative Adversarial Networks [arXiv] [code] [DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-33374-3_4]
S.S. Saravanan, T. Luo, and M.V. Ngo
27th Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (PAKDD), May 2023, pp. 39–54.
Acceptance rate: 16.5% (143/869)
The initial number 822 quoted in the acceptance email was later corrected to 869 in the Conference Summary Report presented at the conference closing ceremony.
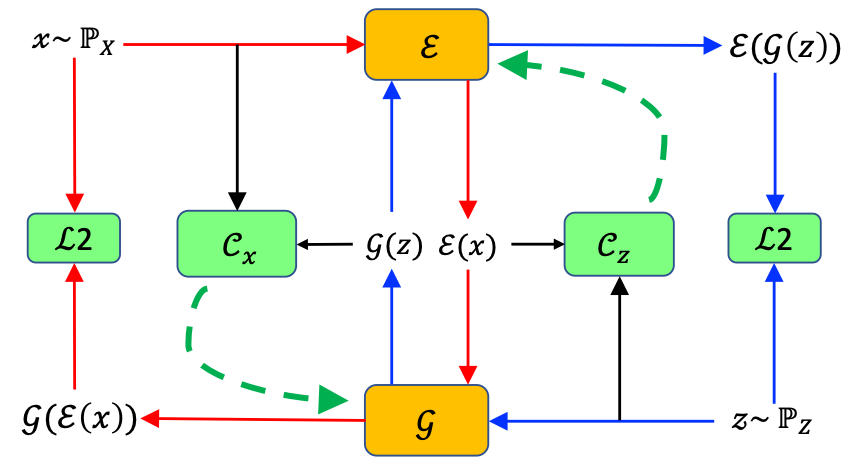
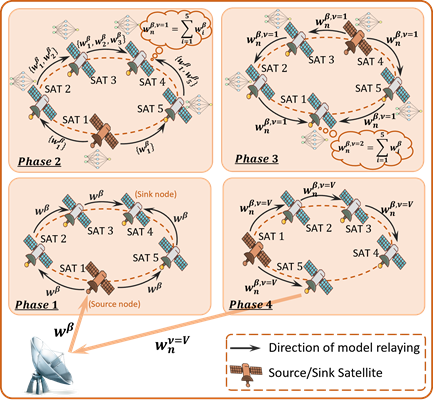
- [ICC'23] Optimizing Federated Learning in LEO Satellite Constellations via Intra-Plane Model Propagation and Sink Satellite Scheduling [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/ICC45041.2023.10279316]
M. Elmahallawy and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), May 2023, pp. 3444-3449.
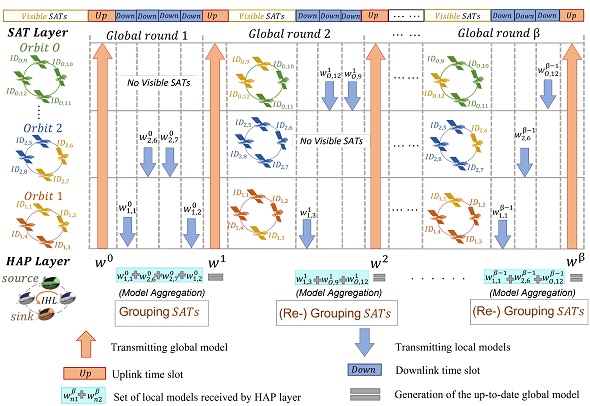
- [BigData'22] AsyncFLEO: Asynchronous Federated Learning for LEO Satellite Constellations with High-Altitude Platforms [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/BigData55660.2022.10021101]
M. Elmahallawy and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on Big Data (BigData), December 2022, pp. 5478-5487.
Acceptance rate: 19% (122/633; full paper)
- [SSCI'22] Learning Deep Representations via Contrastive Learning for Instance Retrieval [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/SSCI51031.2022.10022224]
T. Wu, T. Luo, and D. C. Wunsch
IEEE Symposium Series On Computational Intelligence (SSCI), December 2022, pp. 1501-1506.
- [WCSP'22] FedHAP: Fast Federated Learning for LEO Constellations Using Collaborative HAPs [arXiv] [slides] [DOI: 10.1109/WCSP55476.2022.10039157]
M. Elmahallawy and T. Luo
14th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, November 2022, pp. 888-893.
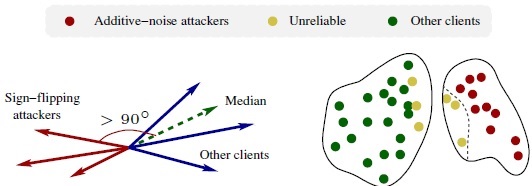
- [ESORICS'22] Long-Short History of Gradients is All You Need: Detecting Malicious and Unreliable Clients in Federated Learning [arXiv] [video] [code] [DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-17143-7_22]
A. Gupta, T. Luo, M. V. Ngo, and S. K. Das
The 27th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS), September 2022, pp. 445-465.
Acceptance rate: 19%
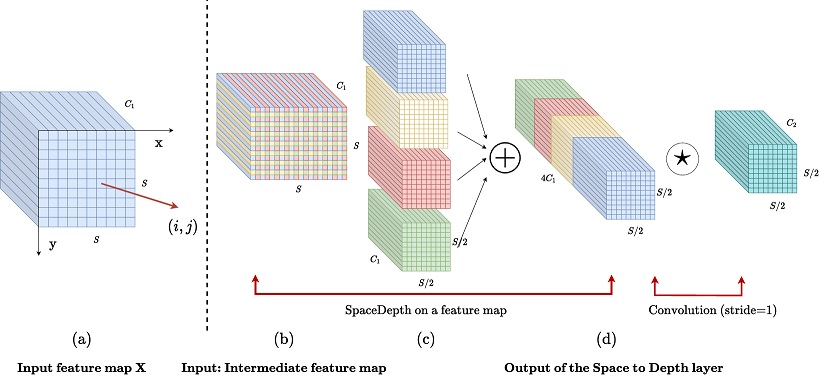
- [ECML PKDD'22] No More Strided Convolutions or Pooling: A New CNN Building Block for Low-Resolution Images and Small Objects [arXiv] [video] [code] [DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-26409-2_27]
R. Sunkara and T. Luo
European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases (ECML PKDD), September 2022, pp. 443-459.
Acceptance rate: 26% (242/932)
- [WiOpt'21] Data-Free Evaluation of User Contributions in Federated Learning [DOI: 10.23919/WiOpt52861.2021.9589136]
H. Lv, Z. Zheng, T. Luo, F. Wu, S. Tang, L. Hua, R. Jia and C. Lv
International Symposium on Modeling and Optimization in Mobile, Ad Hoc, and Wireless Networks (WiOpt), October 2021.
- [AAMAS'21] A Blockchain-Enabled Quantitative Approach to Trust and Reputation Management with Sparse Evidence
L. Zeynalvand, T. Luo, E. Andrejczuk, D. Niyato, S.G. Teo, and J. Zhang
International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS), May 2021.
Acceptance rate: 24.8% (152/612)
- [Globecom'20] Coordinated Container Migration and Base Station Handover in Mobile Edge Computing [arXiv] [video] [code]
M.V. Ngo, T. Luo, H.T. Hoang, and Q.S. Quek
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), December 2020.
- [KDD'20w] Man-in-the-Middle Attacks on MQTT-based IoT Using BERT based Adversarial Message Generation
H. Wong and T. Luo
26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), Workshop on AIoT, August 2020.
- [ICDCS'20] Contextual-Bandit Anomaly Detection for IoT Data in Distributed Hierarchical Edge Computing [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/ICDCS47774.2020.00191]
M.V. Ngo, T. Luo, H. Chaouchi, and Q.S. Quek
IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Demo, December 2020, pp. 1227-1230.
Acceptance rate: 30% (13/43; Demo paper)
- [Huge'20] Scalable Distributed Machine Learning with Huge Data for IoT and Scientific Discovery
T. Luo and S. K. Das
National Science Foundation (NSF) Large Scale Networking Workshop on Huge Data, Chicago, IL, April 13-14, 2020.
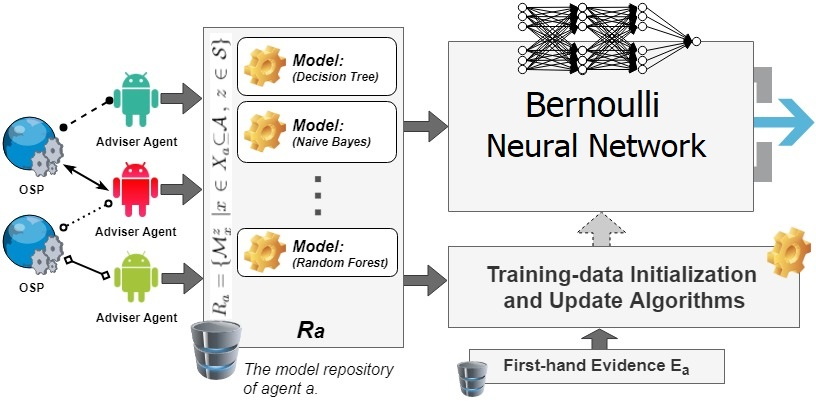
- [AAAI'20] COBRA: Context-aware Bernoulli neural networks for reputation assessment [arXiv]
L. Zeynalvand, T. Luo, and J. Zhang
34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, NY, Feb 7-12, 2020, pp. 7317-7324.
Acceptance rate: 20%
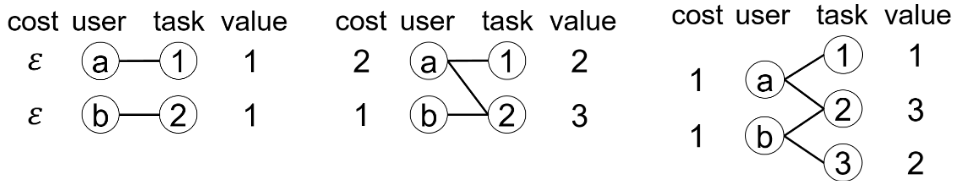
- [AAAI'20] Mechanism design with predicted task revenue for bike sharing systems [arXiv]
H. Lv, C. Zhang, Z. Zheng, T. Luo, F. Wu and G. Chen
34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, NY, Feb 7-12, 2020, pp. 2144-2151.
Acceptance rate: 20%
- [AAAI'20w] Adaptive Anomaly Detection for IoT Data in Hierarchical Edge Computing [arXiv]
M.V. Ngo, H. Chaouchi, T. Luo, and Q.S. Quek
34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), Workshop on AIoT, New York, NY, Feb 2020.
- [AAIM'18] Achieving location truthfulness in rebalancing supply-demand distribution for bike sharing [DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-04618-7_21]
H. Lv, F. Wu, T. Luo, X. Gao, and G. Chen
12th International Conference on Algorithmic Aspects in Information and Management (AAIM), pp. 256-267, December 2018.
Best Student Paper Award (2%; 1/50)
- [FUSION'18] MASA: Multi-Agent Subjectivity Alignment for Trustworthy Internet of Things [DOI: 10.23919/ICIF.2018.8455278]
L. Zeynalvand, J. Zhang, T. Luo, and S. Chen
21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), July 2018, pp. 2013-2020.
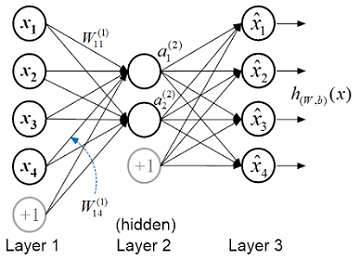
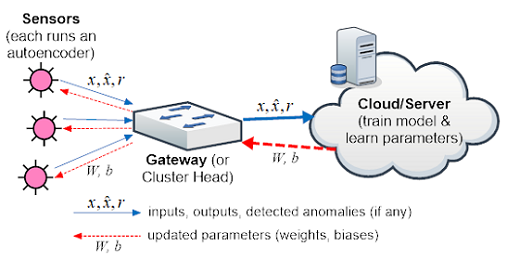
- [ICC'18] Distributed anomaly detection using autoencoder neural networks in WSN for IoT [DOI: 10.1109/ICC.2018.8422402]
T. Luo and S. Nagarajan
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), May 2018.
This paper is the first that introduces autoencoder neural networks, a deep learning model, into wireless sensor networks (WSN) for distributed anomaly detection. It contradicts the general belief that deep learning is not suitable for WSN, by (1) making deep learning extremely shallow and (2) dividing and allocating computation load to sensors and the IoT cloud with a two-part algorithm.
- [Globecom'17] Reshaping mobile crowd sensing using cross validation to improve data credibility [arXiv] [slides] [DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2017.8255050] [Much enhanced version: IoT-J'19]
T. Luo and L. Zeynalvand
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), December 2017.
- [Globecom'16] The privacy exposure problem in mobile location-based services [DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2016.7842319]
F-J. Wu, M. R. Brush, Y-A. Chen, and T. Luo
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), December 2016.
- [IWQoS'16] Selecting most informative contributors with unknown costs for budgeted crowdsensing [DOI: 10.1109/IWQoS.2016.7590447]
S. Yang, F. Wu, S. Tang, T. Luo, X. Gao, L. Kong and G. Chen
IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), June 2016.
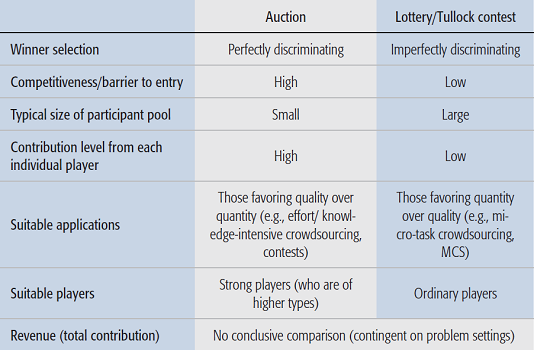
- [INFOCOM'15] Crowdsourcing with Tullock contests: A new perspective [DOI: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2015.7218641]
T. Luo, S. S. Kanhere, H-P. Tan, F. Wu, and H. Wu
The 34th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), April 2015, pp. 2515-2523.
Acceptance rate: 19% (316/1640)
Best Paper Award finalist (0.3%; 5/1640)
What is a Tullock contest? Think it as a lucky draw! While auctions have dominated the realm of mechanism design for decades, this paper suggests Tullock contests as a better alternative, on the basis that it is less competitive and more conducive to larger participation.
 (table from ComMag'17)
(table from ComMag'17)
- [INFOCOM'15] Resisting three-dimensional manipulations in distributed wireless spectrum auctions
D. Peng, S. Yang, F. Wu, G. Chen, S. Tang, and T. Luo
The 34th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), April 2015, pp. 2056-2064.
Acceptance rate: 19% (316/1640)
- [INFOCOM'15w] An endorsement-based reputation system for trustworthy crowdsourcing
C. Wu, T. Luo, F. Wu, and G. Chen
The 34th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), Student Workshop, April 2015, pp. 89-90.
- [Globecom'15] EndorTrust: An endorsement-based reputation system for trustworthy and heterogeneous crowdsourcing [DOI: 10.1109/GLOCOM.2015.7417352]
C. Wu, T. Luo, F. Wu, and G. Chen
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), December 2015.
This reputation system predicts (rather than just evaluates) the quality of user contribution without requiring users' prior contribution. The key to achieving this is to leverage an endorsement relationship among users and use a machine learning technique called collaborative filtering.
- [ICC'15] An efficient and truthful pricing mechanism for team formation in crowdsourcing markets [DOI: 10.1109/ICC.2015.7248382]
Q. Liu, T. Luo, R. Tang, and S. Bressan
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 2015, pp. 567-572.
How to form a team in collaborative crowdsourcing? This paper is the first work that addresses this problem. We design an incentive mechanism called TruTeam to form the "best" team for a cooperative task. We provide theoretical guarantee of its profitability, individual rationality, computational efficiency, and truthfulness.


- [ICC'15] Infrastructureless signal source localization using crowdsourced data for smart-city applications
F-J. Wu and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 2015, pp. 586-591.
- [ISSNIP'15] A crowdsourced WiFi sensing system with an endorsement network in smart cities
F-J. Wu, T. Luo, and Jason Cheah
IEEE 10th International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing (ISSNIP). April 2015, pp. 1-2.
- [MASS'14] Optimal prizes for all-pay contests in heterogeneous crowdsourcing [DOI: 10.1109/MASS.2014.66] [Extended version: TMC'16]
T. Luo, S. S. Kanhere, S. K. Das, and H-P. Tan
The 11th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), October 2014, pp. 136-144.
Acceptance rate: 26.5% (48/181)
- [MASS'14] WiFiScout: A crowdsensing WiFi advisory system with gamification-based incentive [DOI: 10.1109/MASS.2014.32]
F-J. Wu and T. Luo
The 11th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), October 2014, pp. 533-534.
A mobile crowdsensing application called WiFi-Scout is presented in this short paper. This smart-city app provides the WiFi mapping and searching functionalities based on crowdsensed WiFi signals and crowdsourced WiFi user ratings.
- [SMARTCOM'14] A smartphone-based WiFi monitoring system [abstract]
F-J. Wu and T. Luo
Singapore-Japan International Workshop on Smart Wireless Communications (SMARTCOM), October 2014.
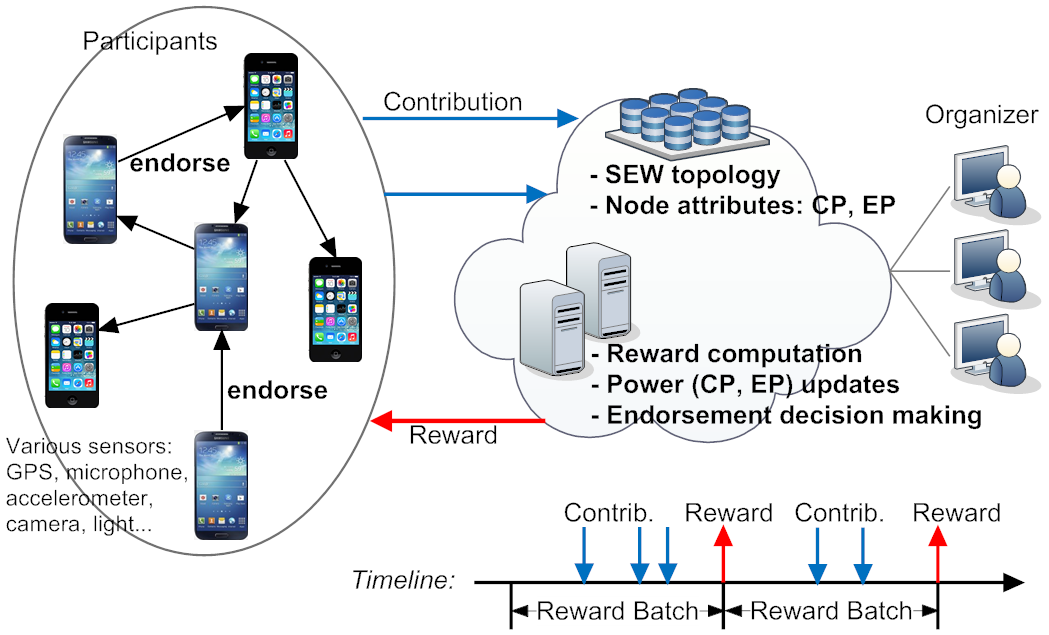
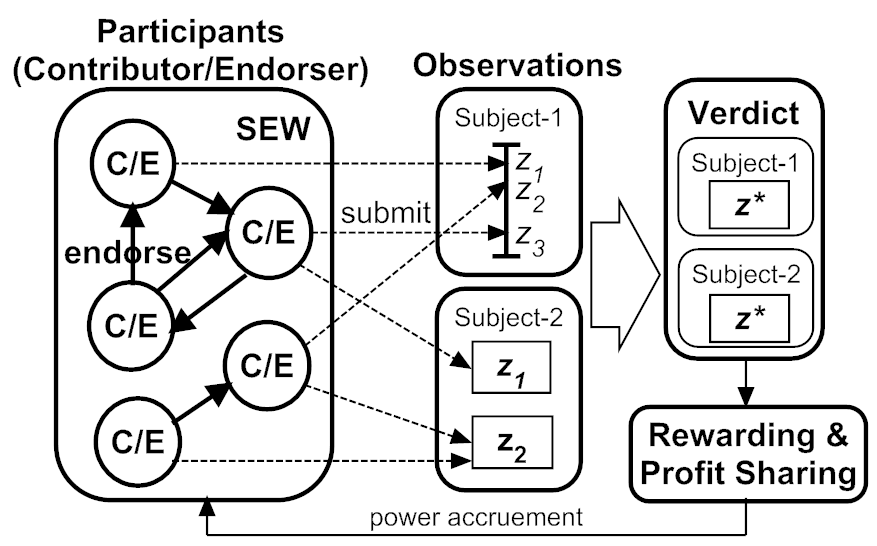
- [SECON'14] SEW-ing a Simple Endorsement Web to incentivize trustworthy participatory sensing [DOI: 10.1109/SAHCN.2014.6990404]
T. Luo, S. S. Kanhere, and H-P. Tan
The 11th IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), July 2014, pp. 636-644.
Acceptance rate: 28.6% (67/234)
This paper introduces an endorsement relationship to connect participants into an socio-economic network to incentivize trustworthy crowdsensing. (SEW has been implemented in two mobile apps, FoodPriceSG and imReporter.)
- [ICC'14] Multi-Channel Directional Medium Access Control for Ad Hoc Networks: A Cooperative Approach
Y. Wang, M. Motani, H. K. Garg, Q. Chen, and T. Luo
IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), June 2014.
- [INFOCOM'14] Profit-maximizing incentive for participatory sensing [DOI: 10.1109/INFOCOM.2014.6847932] [Much enhanced version: ACM TIST'16]
T. Luo, H-P. Tan, and L. Xia
The 33rd IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM), April 2014, pp. 127-135.
Acceptance rate: 19% (319/1650)

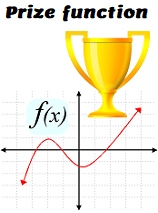 All-pay auction + adaptive prize/reward (see super-abstract of TIST'16).
All-pay auction + adaptive prize/reward (see super-abstract of TIST'16).
- [ISSNIP'14] A generic participatory sensing framework for multi-modal datasets
F-J. Wu and T. Luo
IEEE 9th International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing (ISSNIP), April 2014, pp. 1-6.
- [DCOSS'13] Quality of contributed service and market equilibrium for participatory sensing [Extended version: TMC'15]
C-K. Tham and T. Luo
The 9th IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems (DCOSS), May 2013, pp. 133-140.
Acceptance rate: 27%
- [AsiaCCS'13] Comparative study of multicast authentication schemes with application to wide-area measurement system
Y-W. Law, Z. Gong, T. Luo, S. Marusic, and M. Palaniswami
The 8th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security (AsiaCCS), May 2013, pp. 287-298.
Acceptance rate: 16% (35/216; full paper)
- [SECON'12] Fairness and social welfare in incentivizing participatory sensing [Extended version: COMNET'14]
T. Luo and C-K. Tham
The 9th IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), June 2012, pp. 425-433.
Acceptance rate: 19% (68/350)
- [ICTC'12] Enhancing Responsiveness and Scalability for OpenFlow Networks via Control-Message Quenching [DOI: 10.1109/ICTC.2012.6386857]
T. Luo, H-P. Tan, P. C. Quan, Y-W. Law, and J. Jin
International Conference on Infocom Technology Convergence (ICTC), October 2012, pp. 348-353.
Best Paper Award (0.7%; 3/423)
The OpenFlow switch-controller communication may incur substantial overhead to SDN. We identify such scenarios and propose a solution called CMQ which can tactically suppress a large number of unnecessary control messages (specifically, packet-in from switches and packet-out / flow-mod from the controller).
- [ISCIT'12] Network Architecture and QoS Issues in the Internet of Things for a Smart City
J. Jin, J. Gubbi, T. Luo, and M. Palaniswami
IEEE 12th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), October 2012, pp. 974-979.
- [UCC'11] Participatory cyber physical system in public transport application [Bib]
J. K-S. Lau, C-K. Tham, and T. Luo
Proc. CCSA, IEEE/ACM UCC, December 2011, pp. 355-360.
This paper reports a pilot study in Singapore with a crowd-sensing Android app, called ContriSense:Bus, for public transport.
- [INFOCOM'10W] Dynamic Spectrum Cognitive MAC (DySCO-MAC) for Wireless Mesh & Ad hoc Networks [Bib]
S. Singh, B. De Silva, T. Luo, and M. Motani
IEEE INFOCOM workshop on Cognitive Wireless Communications and Networking, March 2010.
- [SECON'09] Cognitive DISH: Virtual Spectrum Sensing meets Cooperation [Bib]
T. Luo and M. Motani
IEEE SECON, June 2009, pp. 664-672.
Acceptance rate: 18.8% (81/431)
-
T. Luo, M. Motani, and V. Srinivasan
ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing (MobiHoc), May 2008, pp. 43-52.
Acceptance rate: 14.7% (44/300)
Analyzing networking procotols in multi-hop networks is tough, and becomes even harder when it comes to a cooperative protocol. This paper presents a first attempt to address this challenge.
-
T. Luo, M. Motani, and V. Srinivasan
ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom), September 2007.
Acceptance rate: 17% (26 regular papers + 14 extended abstracts out of 233 full-paper submissions)
This paper introduces "altruistic" nodes into multi-channel MAC protocol design, acting as watchdogs to prevent packet collision in ad hoc networks.
- [BroadNets'06] CAM-MAC: A Cooperative Asynchronous Multi-Channel MAC Protocol for Ad Hoc Networks [Extended version: TMC'09]
T. Luo, M. Motani, and V. Srinivasan
International Conference on Broadband Communications, Networks and Systems (BroadNets), October 2006, pp. 1-10.
- [Globecom'03] Analyses and improvements of link management protocol for GMPLS-based networks
T. Luo and G-S. Kuo
IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), December 2003, pp. 2992-2998.
- [ICCT'03] SLA foundation template library: reusable-component repository for SLA
T. Luo and L. Meng
IEEE 9th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), April 2003, pp. 1739-1743.
- [ICCT'03] Two novel 2x2 models for MEMS-based optical switches
T. Luo
IEEE 9th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), April 2003, pp. 597-600.
- [JSAC'24] Communication-Efficient Federated Learning for LEO Satellite Networks Integrated with HAPs using hybrid NOMA-OFDM [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/JSAC.2024.3365885]
M. Elmahallawy, T. Luo, and K. Ramadan
IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications (JSAC), Vol. 42, No. 5, pp. 1097-1114, May 2024.
- [ComMag'23] Catching Elusive Depression via Facial Micro-Expression Recognition [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2300003]
X. Chen and T. Luo
IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 61, no. 10, pp. 30-36, October 2023.
- [Pattern'23] YOGA: Deep Object Detection in the Wild with Lightweight Feature Learning and Multiscale Attention [arXiv] [code] [DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109451]
R. Sunkara and T. Luo
Pattern Recognition, vol. 139, pp. 109451, July 2023.
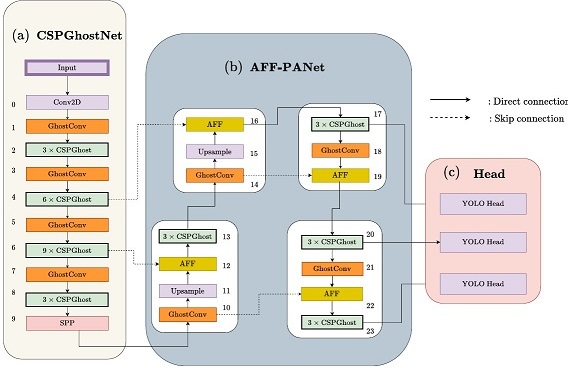
- [ARAI'23] Black-Box Attack using Adversarial Examples: A New Method of Improving Transferability [DOI: 10.1142/S2811032322500059]
T. Wu, T. Luo, and D. C. Wunsch
World Scientific Annual Review of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 1, pp. 2250005, February 2023.
- [TIOT'21] Adaptive Anomaly Detection for Internet of Things in Hierarchical Edge Computing: A Contextual-Bandit Approach [video] [DOI: 10.1145/3480172]
M.V. Ngo, T. Luo, and Q.S. Quek
ACM Transactions on Internet of Things (TIOT),
Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 1-23, October 2021.

- [TOPS'20] CrowdPrivacy: Publish More Useful Data with Less Privacy Exposure in Crowdsourced Location-based Services [DOI: 10.1145/3375752]
F-J. Wu and T. Luo
ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security (TOPS),
Vol. 23, No. 1, pp. 6:1-25, February 2020.
- [TCS'20] Hardness of and Approximate Mechanism Design for the Bike Rebalancing Problem [DOI: 10.1016/j.tcs.2019.07.030]
H. Lv, F. Wu, T. Luo, X. Gao and G. Chen
Theoretical Computer Science (TCS), vol. 803, pp. 105-115, January 2020.
- [IoT-J'19] Improving IoT data quality in mobile crowd sensing: A cross validation approach [DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2904704]
T. Luo, J. Huang, S. S. Kanhere, J. Zhang, and S. K. Das
IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IoT-J), vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 5651-5664, June 2019.
A cross validation (CV) approach that seeks a validating crowd to ratify the quality of sensor data contributed by the a contributing crowd. By making an exploration-exploitation tradeoff, a unified solution is offered to two disparate cases: reinforce obscure truth and discover hidden truth.
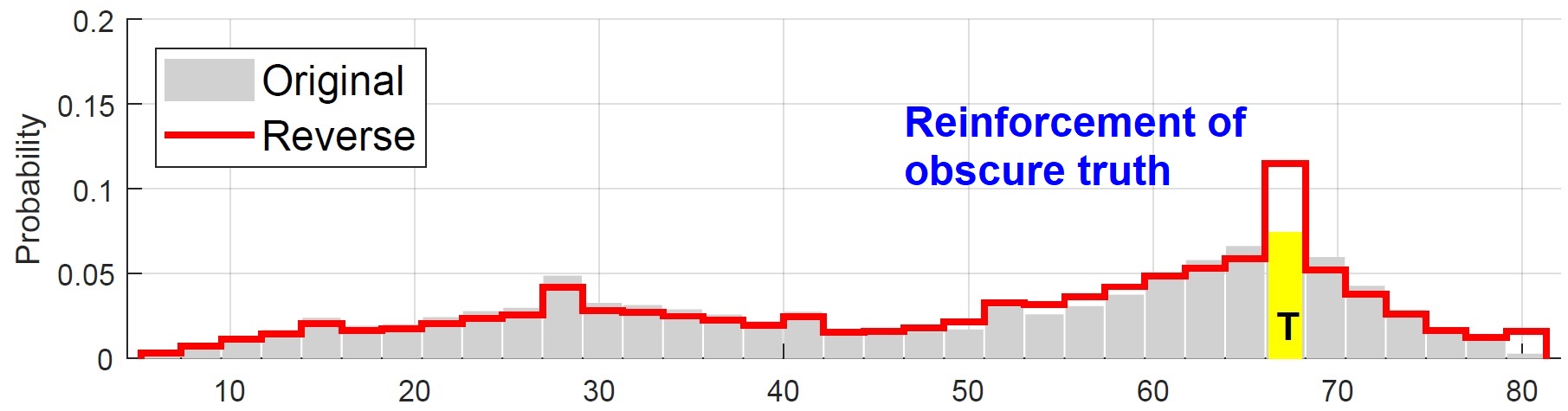
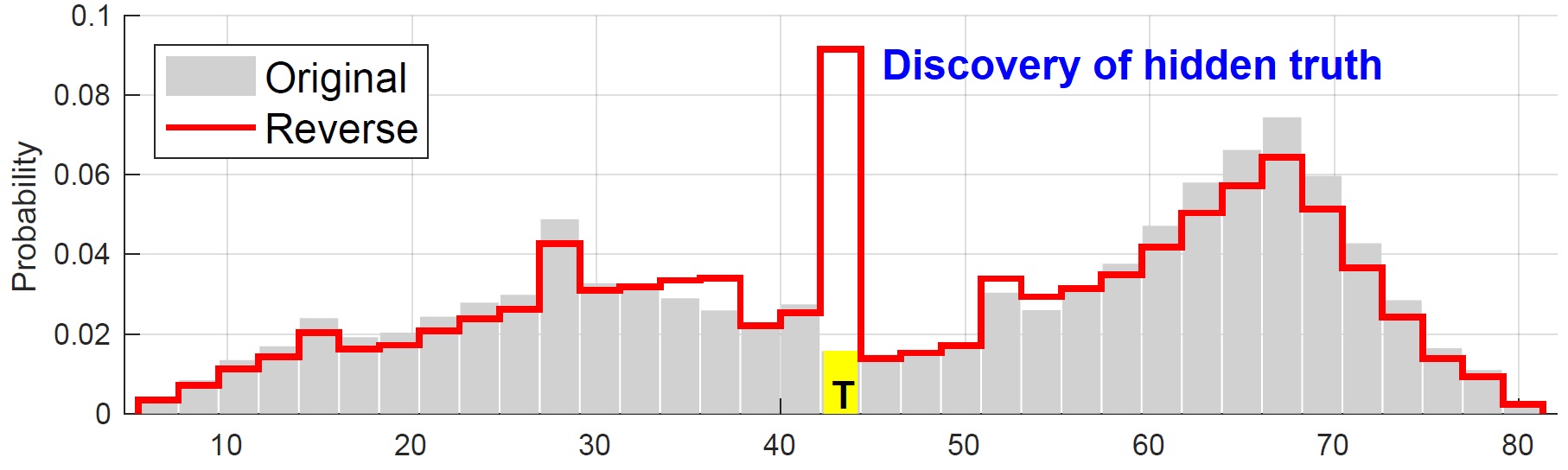
- [TMC'19] On designing distributed auction mechanisms for wireless spectrum allocation [DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2018.2869863]
S. Yang, D. Peng, T. Meng, F. Wu, G. Chen, S. Tang, Z. Li, and T. Luo
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), vol. 18, no. 9., pp. 2129-2146, September 2019.
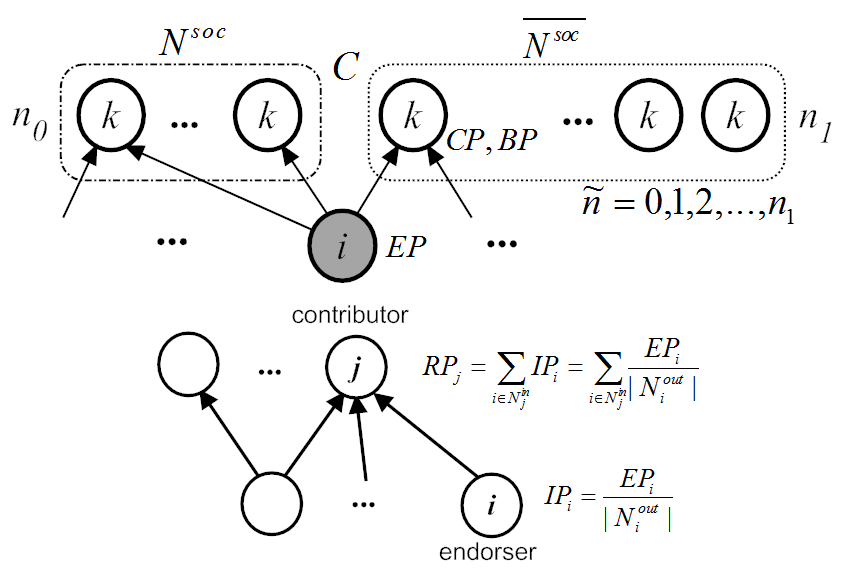
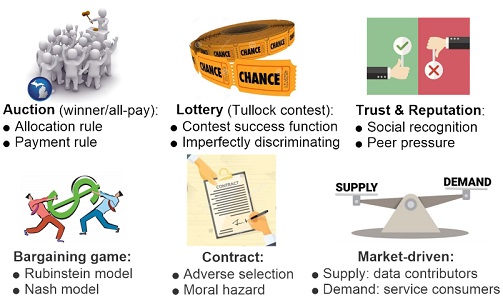
- [ComMag'17] Sustainable incentives for mobile crowdsensing: Auctions, lotteries, and trust and reputation systems [arXiv] [DOI: 10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600746CM]
T. Luo, S. S. Kanhere, J. Huang, S. K. Das, and F. Wu
IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 68-74, March 2017.
This survey paper provides a technical overview and analysis of six incentive mechanism design frameworks: auction, lottery, trust and reputation system, bargaining game, contract theory, and market-driven mechanism.

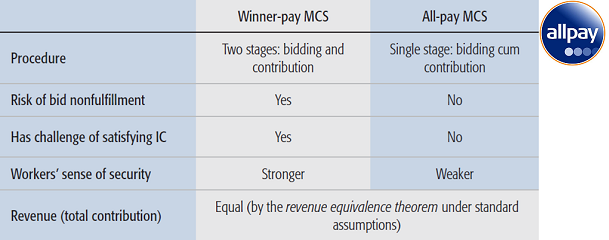
- [TIST'16] Incentive mechanism design for crowdsourcing: an all-pay auction approach [DOI: 10.1145/2837029] [Appendix]
T. Luo, S. K. Das, H-P. Tan, and L. Xia
ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 35:1-26, February 2016.
The most adopted auctions in incentive mechanism design so far have been winner-pay auctions (WPA), in which only winners (who outbid others and will therefore receive reward) need to pay their bids. By contrast, all-pay auctions (APA) require all the participants regardless of who win the auction to pay their bids. This apparently sounds unreasonable, but when applied to crowdsourcing, it makes perfect sense and gains two important advantages over WPA. (This paper is a substantial extension of INFOCOM'14.)
 (table from our ComMag'17 paper)
(table from our ComMag'17 paper)
- [TMC'16] Incentive mechanism design for heterogeneous crowdsourcing using all-pay contests [DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2015.2485978] [Appendix]
T. Luo, S. S. Kanhere, S. K. Das, and H-P. Tan
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 2234-2246, September 2016.
Despite that crowdworkers are typically heterogeneous (in abilities, costs, etc.), the daunting challenge of modeling and analyzing such scenarios has restricted researchers to choosing homogeneous models in which all the worker types follow a single, common distribution (Bayesian belief). This paper addresses this challenge using an asymmetric all-pay auction model with a prize tuple. Not only does it achieve better performance, but it also uncovers a counter-intuitive and interesting property called strategy autonomy, in which the asymmetric equilibrium collapses into a symmetric one.


- [TMC'16] Competition-based participant recruitment for delay-sensitive crowdsourcing applications in D2D networks [DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2016.2524590]
Y. Han, T. Luo, D. Li, and H. Wu
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), vol. 15, no. 12, pp. 2987-2999, December 2016.
To reduce the large delay in Device-to-Device (D2D) networks, two distributed approaches were proposed that closely approximate a centralized, dynamic programming algorithm: (1) divide-and-conquer with Voronoi cells, (2) task splitting and delegation.
- [Syst'16] Cooperative Multichannel Directional Medium Access Control for Ad Hoc Networks [DOI: 10.1109/JSYST.2015.2478801]
Y. Wang, M. Motani, H. K. Garg, Q. Chen, and T. Luo
IEEE Systems Journal, 2016.
- [JSAN'16] Cloud-Enhanced Robotic System for Smart City Crowd Control [html]
A. Rahman, J. Jin, A. Cricenti, A. Rahman, M. Palaniswami, and T. Luo
Journal of Sensor and Actuator Networks, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1-26, December 2016.
- [TMC'15] Quality of contributed service and market equilibrium for participatory sensing [DOI: 10.1109/TMC.2014.2330302]
C-K. Tham and T. Luo
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 829-842, April 2015.
Characterizing QoS for crowdsensing is a challenge, and this work proposes a new metric called Quality of Contributed Service (QCS) to aggregate individual quality of contributions by taking information quality and time sensitivity into account. We analyze this metric using a market-based supply-and-demand model.
- [COMNET'14] Fairness and social welfare in service allocation schemes for participatory sensing [DOI: 10.1016/j.comnet.2014.07.013]
C-K. Tham and T. Luo
Computer Networks, Elsevier, vol. 73, pp. 58-71, November 2014.
Instead of using monetary or reputation-based incentives, this paper proposes a resource-allocation approach to incentivize crowdsensing. Specifically, it allocates each user certain "service quota" based on the user's contribution level and all the users' service demands.
- [SMC'13] Sensing-Driven Energy Purchasing in Smart Grid Cyber-Physical System
C-K. Tham and T. Luo
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems (SMC), vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 773-784, July 2013.
We design an optimizer and decision maker for each household to optimize their electricity purchase from the main grid. It takes sensing data as input and uses multi-stage stochastic programming as well as linear programming to perform the optimization.
- [CommLett'12] Sensor OpenFlow: Enabling Software-Defined Wireless Sensor Networks
T. Luo, H-P. Tan, and Q.S. Quek
IEEE Communications Letters, vol. 16, no. 11, pp. 1896-1899, November 2012.
This work is the first that introduces software-defined networking (SDN) into wireless sensor networks, where a Sensor OpenFlow protocol within a SD-WSN architecture was proposed.
- [TMC'12] Energy-Efficient Strategies for Cooperative Multi-Channel MAC Protocols [Bib]
T. Luo, M. Motani, and V. Srinivasan
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 553-566, April 2012.
As a substantial extension of MobiCom'07 (see super-abstract there), this journal version thoroughly investigates the energy aspect of the MobiCom'07 paper.
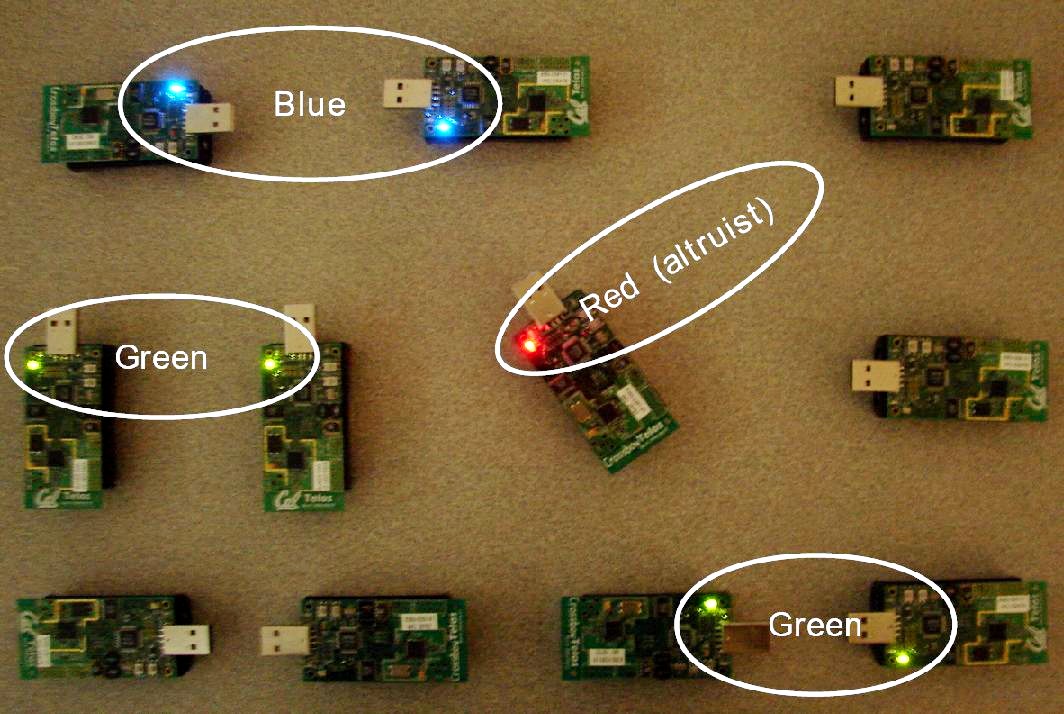 (TelosB implementation)
(TelosB implementation)
- [TMC'10] A Metric for DISH Networks: Analysis, Implications, and Applications [Bib]
T. Luo, V. Srinivasan, and M. Motani
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 376-389, March 2010.
This paper gives an example of how to analyze cooperative networking procotols. The key idea is to introduce a metric called pco, which is the availability of cooperation or more specifically the probability of obtaining cooperation. We then provide an analysis of pco in both single-hop and multi-hop networks.
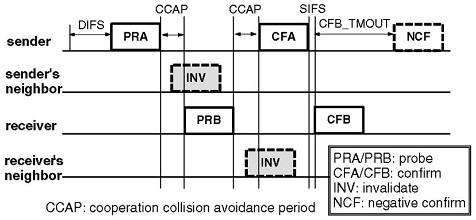
- [TMC'09] Cooperative Asynchronous Multichannel MAC: Design, Analysis, and Implementation [Bib]
T. Luo, M. Motani, and V. Srinivasan
IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC). Vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 338-352, March 2009.
Remark: The proposed protocol (CAM-MAC) was subsequently implemented by Shashi R. Singh on a mesh network testbed demonstrated at MobiCom'10 (program). The detailed report can be found here (WiNTECH program).


















 (table from ComMag'17)
(table from ComMag'17)





 All-pay auction + adaptive prize/reward (see super-abstract of TIST'16).
All-pay auction + adaptive prize/reward (see super-abstract of TIST'16).








 (table from our ComMag'17 paper)
(table from our ComMag'17 paper)



 (TelosB implementation)
(TelosB implementation)![]() Google Scholar
Google Scholar![]() Code
Code